|
Detail Information |
|||
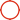
Product Description
High-performance Discharge rate Sodium Ion Batteries 3.2V Nominal Voltage
Product Description:
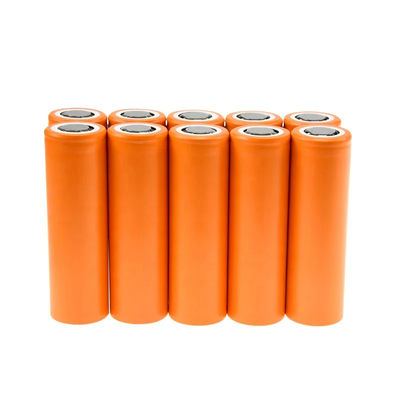
26650 Sodium Ion Batteries 3.2V Nominal Voltage Long Cycle Life Short Recharge Time
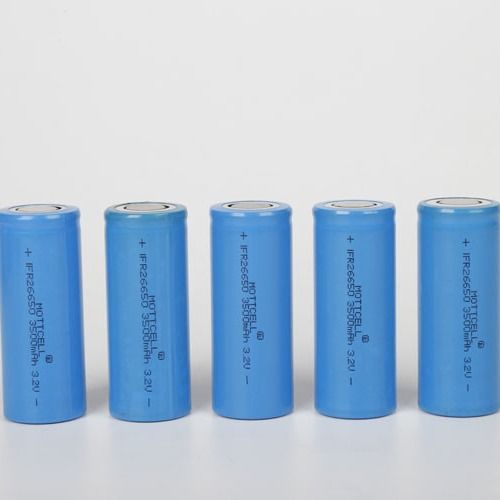

Sodium-ion batteries are gaining attention as a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. They offer several advantages. First, sodium is relatively inexpensive and more abundant than lithium. Additionally, sodium-ion batteries exhibit good safety characteristics, with the potential for high energy density and long cycle life.
These batteries present opportunities for a more sustainable and efficient energy future. They can be employed in renewable energy storage, electric vehicles, and grid-scale energy storage.
Features:

Due to the abundance and low cost of sodium, these batteries serve as a cost-effective substitute for lithium-ion technology. They not only boast significant economic advantages but also demonstrate impressive safety and stability, mitigating the risks of thermal runaway and explosion.
Aside from strong safety traits, sodium-ion batteries feature noteworthy energy density. This means they can store substantial amounts of energy within a relatively small volume. Moreover, they possess a long cycle life, ensuring minimal capacity loss during charging and discharging processes.
Given these superior features, sodium-ion batteries are viewed as a practical option for renewable energy storage, electric vehicles, and grid-scale energy management. Their deployment in these sectors will contribute to a more sustainable and efficient utilization of energy resources.
Technical Parameters:
| Parameter | Detail |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | -20~55˚C |
| Nominal Voltage | 3.2V |
| Discharge rate | ≥4C |
| Safety | High |
| Size | 26650 |
| Energy Density | 140Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | Long |
| Capacity | 2300mAh |
| Cut-off Discharge Volt | 1.5V |
| Recharge Time | Short |
Applications:
26650 Sodium Ion Batteries 3.2V Nominal Voltage Long Cycle Life Short Recharge Time
Used in power tools, lighting, wind and solar energy storage, electric vehicles, toys, instrumentation, UPS backup power supplies, communication devices, medical equipment, and military lighting applications
Packing and Shipping:
Sodium ion batteries need to be packaged and shipped with care to ensure product integrity and safety. The following steps should be taken to ensure proper packaging and shipping:
- Pack batteries in an insulated container with air-cushioning material between each battery to prevent shifting during transport.
- Make sure the container is sealed and securely closed.
- Label the container with warning symbols and the words ‘Hazardous Materials’.
- Ensure the container is adequately protected against shocks, vibration, and extremes of temperature.
- Ship the container using a reliable carrier with a tracking system.
FAQ:
Q1:What is a sodium-ion battery?
A1:A sodium-ion battery is a new type of battery technology that uses sodium ions as the charge carrier, instead of the traditional lithium ions. This battery has potential high energy density and longevity, as well as the use of safer and more environmentally friendly electrolytes.
Q2:What are the advantages of a sodium-ion battery?
A2:Sodium-ion batteries have some important advantages. Firstly, they have high energy density, which means they can store more electrical energy. Secondly, sodium-ion batteries charge faster and can be charged more quickly. In addition, sodium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan and can be used repeatedly for a longer time. Finally, sodium-ion batteries use safer and more environmentally friendly electrolytes, resulting in less environmental impact.
Q3:What are the differences between a sodium-ion battery and a lithium-ion battery?
A3:The main difference between a sodium-ion battery and a lithium-ion battery is that they use different anode and cathode materials. Lithium-ion batteries use lithium metal as the anode, while sodium-ion batteries use sodium metal as the anode. In addition, the electrolyte of a sodium-ion battery is also different from that of a lithium-ion battery.
Q4:What applications can a sodium-ion battery be used for?
A4:Sodium-ion batteries can be used in many applications. They can be used for power storage systems, such as in renewable energy systems like wind and solar energy. In addition, they can also be used in electric vehicles and electronic devices.
Q5:What are the future trends in the development of sodium-ion batteries?
A5:The future trends in the development of sodium-ion batteries are to improve energy density and lifespan, reduce costs, and achieve large-scale production. In addition, researchers are exploring new electrolyte and electrode materials to further improve the performance and safety of the battery.